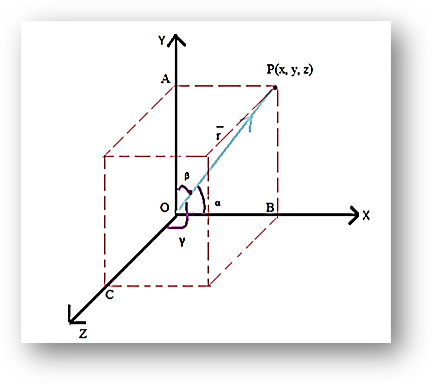
Direction Cosines When a directed line OP O as the reference, these angles are referred as the direction angles of the line and the cosine of these angles give us the direction cosines. These direction cosines are usually represented as l, m and n.
If we extend the line OP on the three dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, then to figure out the direction cosines, we need to take the supplement of the direction angles. It is pretty obvious from this statement that on reversal of the line OP in opposite direction, the direction cosines of the line also get reversed. In a situation where the given line does not pass through the origin, a line parallel to the given line passing through the origin is drawn and in doing so, the angles remain same as the angles made by the original line. Hence, we get the same direction.
Since we are considering a line passing through the origin to figure out the direction angles and their cosines, we can consider the position vectors of the line OP.
If OP = r , then from the above figure 1, we can see that
\(\begin{array}{l}x \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}r cos \alpha\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}y\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} r cos \beta\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}z\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} r cos \gamma\end{array} \)
Where r denotes the magnitude of the vector and it is given by,
\(\begin{array}{l}r\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{(x – 0)^2 + (y – 0)^2 + (z – 0)^2}\end{array} \) \(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow r\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} \sqrt{x^2 + y^2 + z^2}\end{array} \)
The cosines of direction angles are given by
\(\begin{array}{l}cos \alpha\end{array} \) , \(\begin{array}{l}cos \beta\end{array} \) and \(\begin{array}{l}cos\gamma\end{array} \)
and these are denoted by l, m and n respectively. Therefore, the above equations can be reframed as:
\(\begin{array}{l}x\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}r cos\alpha\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} lr\end{array} \) ——————————————————— (1)
\(\begin{array}{l}y\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} r cos\beta\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} mr \end{array} \) ——————————————————– (2)
\(\begin{array}{l}z\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}r cos \gamma\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} nr \end{array} \) ——————————————————— (3)
We can also represent r in terms of its unit vector components using the orthogonal system.
\(\begin{array}{l}r\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} x\hat{i} + y \hat{j} + k \hat{z}\end{array} \)
Substituting the values of x, y and z, we have
\(\begin{array}{l}r \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} lr\hat{i} + mr\hat{j} + nr\hat{z}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \hat{r}\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} \frac{r}{|r|}\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} l\hat{i} + m\hat{j} + n \hat{z}\end{array} \)
Therefore, we can say that cosines of direction angles of a vector r are the coefficients of the unit vectors \(\begin{array}{l}\hat{i}\end{array} \) , \(\begin{array}{l} \hat{j}\end{array} \) and \(\begin{array}{l}\hat{k}\end{array} \) when the unit vector \(\begin{array}{l}\hat{r}\end{array} \) is resolved in terms of its rectangular components.
Any number proportional to the direction cosine is known as the direction ratio of a line. These direction numbers are represented by a, b and c.
Also as
\(\begin{array}{l}OP^2\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} OA^2 + OB^2 + OC^2 \end{array} \)
In simple terms,
\(\begin{array}{l}r\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{x^2 + y^2 + z^2}\end{array} \)
On dividing the equation,
\(\begin{array}{l}r^2 \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} x^2 + y^2 + z^2~ by ~r^2 \end{array} \)
we have,
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{r^2}{r^2} \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} \frac{x^2}{r^2} + \frac{y^2}{r^2} + \frac{z^2}{r^2}\end{array} \)
Using equations 1, 2 and 3, we get
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 1 \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}(\frac{x}{r})^2 + (\frac{y}{r})^2 + (\frac{z}{r})^2\end{array} \)
= \(\begin{array}{l}l^2 + m^2 + n^2\end{array} \)
We can conclude that sum of the squares of the direction cosines of a line is 1.
From the above definition, we can say that
\(\begin{array}{l}a ∝ l\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}b ∝ m\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}c ∝ n\end{array} \)
From these relations, we get
\(\begin{array}{l} a \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} kl\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} b \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} km\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} c \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} kn\end{array} \)
The ratio between the direction cosines and direction ratios of a line is given by
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{l}{a} \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{m}{b}\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{n}{c}\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}k\end{array} \)
But we know that
\(\begin{array}{l}l^2 + m^2 + n^2 \end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l}1\end{array} \)
From this, we can find that
\(\begin{array}{l}k\end{array} \) = \(\begin{array}{l} \pm \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2 + b^2 + c^2}}\end{array} \)
The value of k can be chosen as positive or negative depending upon the direction of the directed line.
We can take any number of direction ratios by altering the value of k.
📌 Related Posts:
Linear Programming-Definition, Methods & Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
|
Independent & Mutually Exclusive Events in Probability-Definition, Venn Diagram & Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
|
Increasing & Decreasing Functions Monotonicity with Examples for Functions, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
|
Types of Linear Programming Problems | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
|
Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions-Definition, Formula, Properties, Rules, Graphs, Derivatives, Exponential Series & Solved Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
📋 Explore More:
-- Choose a post --
Relations & Functions-Types of Functions: Classification, One-One, Onto, Examples-Class 12 Math Chapter 1 Notes Download free pdf
Composite functions-Relations & functions Class 12 Math Chapter 1 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Invertible Functions-Graph, Solved Examples & FAQs, Relations & functions Class 12 Math Chapter1 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Composition of Functions: Definition, Domain, Range, Examples, Relations & functions Class 12 Math Chapter 1 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Inverse Functions, Graphs & Solved Examples, Relations & functions Class 12 Math Chapter 1 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Inverse Trigonometric Functions-Formulas, Types, Graphs & Solved Examples, Class 12 Math Chapter 2 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Graphs of Inverse Trigonometric Functions-Formulas, Solved Examples, Class 12 Math Chapter 2 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions-Formulas, Solved Examples, Class 12 Math Chapter 2 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Inverse Trigonometric Identities-Domain, Range, Formulas, Properties, Solved Examples, Class 12 Math Chapter 2 Notes Study Material Download free pdf
Relations & Functions Exercise 1.1 NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 1 free PDF Download
Relations & Functions Exercise 1.2 NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 1 free PDF Download
Relations & Functions Exercise 1.3 NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 1 free PDF Download
Relations & Functions Miscellaneous Exercise NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 1 free PDF Download
Matrices Exercise 3.1 NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 3 free PDF Download
Matrices Exercise 3.2 NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 3 free PDF Download
Matrices Exercise 3.3 NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 3 free PDF Download
Matrices Miscellaneous Exercise NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Chapter 3 free PDF Download
Matrices Definition, Properties, Types, Formulas, Solved Examples
Matrices Types, Properties:Row, Column, Zero or Null, Singleton, Horizontal, Vertical, Square, Diagonal, Scalar, Unit or Identity Matrix, Equal Matrices, Triangular, Singular & Non-Singular Matrix, Symmetric & Skew Symmetric Matrices, Hermitian & Skew-Hermitian Matrices, Idempotent, Nilpotent, Periodic, Involutory Matrix
Algebra of Matrices:Addition, Subtraction, Scalar Multiplication, Matrices Multiplication, Rules & Solved Examples
Transpose of a Matrix-Addition & Multiplication Property of Transpose, Solved Examples
Symmetric & Skew Symmetric Matrix-Properties, Solved Examples
Elementary Operation of Matrix with Solved Examples-Class 12 Math Matrices Notes
Invertible Matrices | Invertible Matrix Theorems, Proofs, Applications & Properties, Solved Examples, Class 12 Matrix Notes
Determinants-Properties-Differentiation and Integration of Determinants-Class 12 Math Notes Study Material free pdf download
Determinant To Find Area Of A Triangle – Solved Examples-Class 12 Math Determinants Notes Study Material free pdf download
Minors and Cofactors in Matrix with Solved Examples Problems-Class 12 Math Determinants Notes Study Material free pdf download
Adjoint and Inverse of a Matrix With Their Relation, Properties, Solved Examples Problems, Class 12 Math Determinants Notes Study Material free pdf download
Continuity and Differentiability of a Function-Solved Examples Problems, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material free pdf download
Exponential Functions, Logarithmic Functions-Definition, Formula, Properties, Rules, Graphs, Derivatives, Exponential Series & Solved Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Logarithmic Differentiation – Formula, Solutions & Solved Examples Problems, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Derivatives Of A Function In Parametric Form-Solved Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Second Order Derivative | Explanation with Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Mean Value Theorem Formula Equation | Mean Value Theorem For Integrals, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Increasing & Decreasing Functions Monotonicity with Examples for Functions, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Equation of Tangent And Normal to a Curve with Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Differential Calculus & Approximation | Tangent Line Approximation, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integral Calculus – Definition, Formulas, Methods, Applications, Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integration in Maths – Definition, Formulas and Types, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integrals | Definition, Meaning, Formula, Application and Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integration by Substitution Method – Formula, Examples & Questions, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integration by Partial Fractions – Method, Examples & Practice Problems, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integration by Parts | Formula, Derivation and Examples, Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integration by Substitution Formula | Sample Problems | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integral of Particular Functions (With Proof and Example) | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Partial Fraction in Integration – Definition, Formula, Decomposition, Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Integration by Parts – Formula, ILATE Rule & Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Definite Integral – Definition, Formulas, Properties and Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Area Under The Curve Using Integration | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Area under Curves – Tricks for Solving Area under Curves | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Application of Integrals MCQs (With Answers) | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Indefinite Integrals MCQs With Answers | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Important Integration Questions With Answers | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Area Between Two Curves Using Integration | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Differential Equations | Types, Order, Degree, Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Types of Differential Equations | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Solution Of A Differential Equation -General & Particular | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Separable Differential Equation-Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Vectors in Maths-Unit Vector, Zero or null Vector, Magnitude of Vector, Operations on Vectors, Dot product of Vectors, Scalar Triple Product
Types of Vectors | Zero Vector, Unit Vector, Position Vector, Co-initial Vector, Like & Unlike Vectors, Co-planar Vectors, Collinear Vectors, Equal Vectors, Displacement Vector, Negative of a Vector
Laws of Vector Addition- Parallelogram, Triangle Law, Vector Addition | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Multiplication Of Vectors by a Scalar Quantity with examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Scalar or Dot Product Of Two Vectors | Projection of Vector | Definition, Properties, Formulas and Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Equation of Line in Three Dimensions | Cartesian & vector Equation | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Angles Between two Lines in 3D Space: Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Shortest Distance Between Two Lines in 3D Space, Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Probability-Definition, Formula, Types, Problems & Solutions | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Conditional Probability, Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Multiplication Rule of Probability | Proof & Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Independent & Mutually Exclusive Events in Probability-Definition, Venn Diagram & Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Bayes Theorem | Definition, Proof, Formula, Derivation & Solved Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Probability Distribution | Definition, Types, Formula, Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Probability Bernoulli Trial & Binomial Distribution of Random Variables | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Linear Programming-Definition, Methods & Examples | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Linear Programming Problem LPP-Simplex & Graphical Method | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF
Types of Linear Programming Problems | Class 12 Math Notes Study Material Download Free PDF